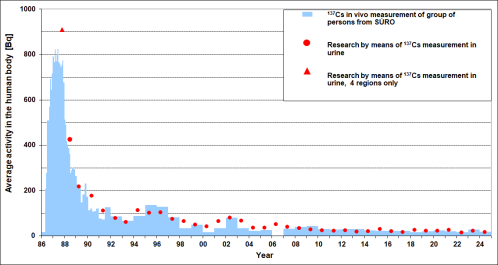
Evolution of content of 137 Cs at Czech population after the Chernobyl accident
Every year, a monitoring of an internal contamination with 137Cs is carried out in SÚRO Prague, CZ. The monitoring is performed in a whole-body counting laboratory on a reference group of 30 people (15 males and 15 females), mainly Prague inhabitants between the ages of 28 and 70 years (in the year of 2024). Based on those measurements in the year of 2024, the average activity of 137Cs in an individual body has been estimated to be 19 Bq. As in previous years, a national survey of internal contamination with 137Cs has been carried out based on the urinary excretion of 137Cs in 24-hour urine samples. Urine samples were collected from 35 males and 35 females, representatives of average population by their diet. Average activity of 137Cs excreted in 24-hour urine sample is 0.104 Bq, resulting in the calculated 137Cs average body content (retention) of 17 Bq. Based on the results from the national survey, the committed effective dose from 137Cs is estimated to be 0.61 μSv. The development in time of the average 137Cs retention obtained from the both data sets since the year 1986 is given in the picture.
A specific group of hunters, representatives of a population with special dietary habits (comsuption of wild boar meat), has been measured again in 2024. A standard whole body in vivo measurement has been, however, skipped this year due to low radiocaesium intakes in the group during last few years which lead to nonsignificant results of radiocaesium activity in a body. Intake of radiocaesium by the group in 2024 was estimated from an analysis of 24h urine samples collected from the members of the group. The average individual intake of 517 Bq results in the individual committed effective dose of 6.7 μSv.